
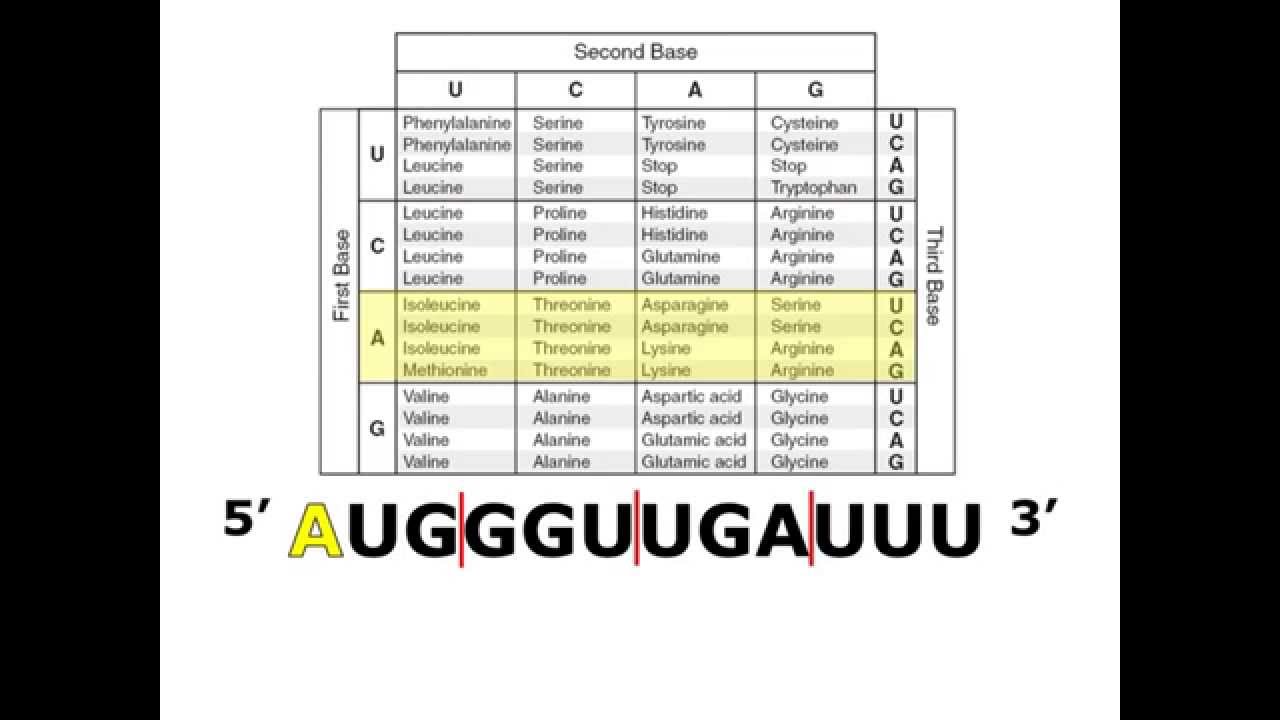
The amino acid sequence of proteins from all types of organisms is usually determined by sequencing the gene that encodes the protein and then reading the genetic code from the DNA sequence. A look at the genetic code in the codon table below reveals that the code is redundant meaning many of the amino acids can be coded by four or six possible codons. A codon table can therefore be constructed and any coding region of nucleotides read to determine the amino acid sequence of the protein encoded. Youll see that many amino acids are actually encoded by more than one codon. That means all organisms use the same codons to specify the placement of each of the 20 amino acids in protein formation. Take a look at the chart below showing which codons encode which amino acids.
AMINO ACID SEQUENCE CHART MRNA CRACKED
The genetic code only needed to be cracked once because it is universal (with some rare exceptions). These three letter codes of nucleotides (AUG, AAA, etc.) are called codons. When experiments were performed to crack the genetic code it was found to be a code that was triplet. For example, there are six ways to write leucine in mRNA language. A triplet code could make a genetic code for 64 different combinations (4 X 4 X 4) genetic code and provide plenty of information in the DNA molecule to specify the placement of all 20 amino acids. It can be seen that many amino acids are shown in the table by more than one codon. Translation Practice Directions Using a codon chart, match the mRNA codons with their correction amino acid sequence. Find out the amino acid sequence that can be assembled from the mRNA associated with the.

A doublet code could code for 16 amino acids (4 x 4). The sequence of a protein is usually notated as a string of letters, according to the order of the amino acids from the amino-terminal to the carboxyl-terminal of the protein. Complete the following chart using your genetic code chart worksheet. Each codon is read from 3 (first nucleotide) to 5 (third nucleotide). Since there are only four nucleotides, a code of single nucleotides would only represent four amino acids, such that A, C, G and U could be translated to encode amino acids. DNA utilizes four bases, adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T), in its code. The logic is that the nucleotide code must be able to specify the placement of 20 amino acids. DNA is used as a template for the cell to build mRNA. Prior to understanding the details of transcription and translation, geneticists predicted that DNA could encode amino acids only if a code of at least three nucleotides was used.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
